[Python SE] Binary Tree and BST in Python
21/01/25 - #softwareengineering #pyhton #bst #binarytree
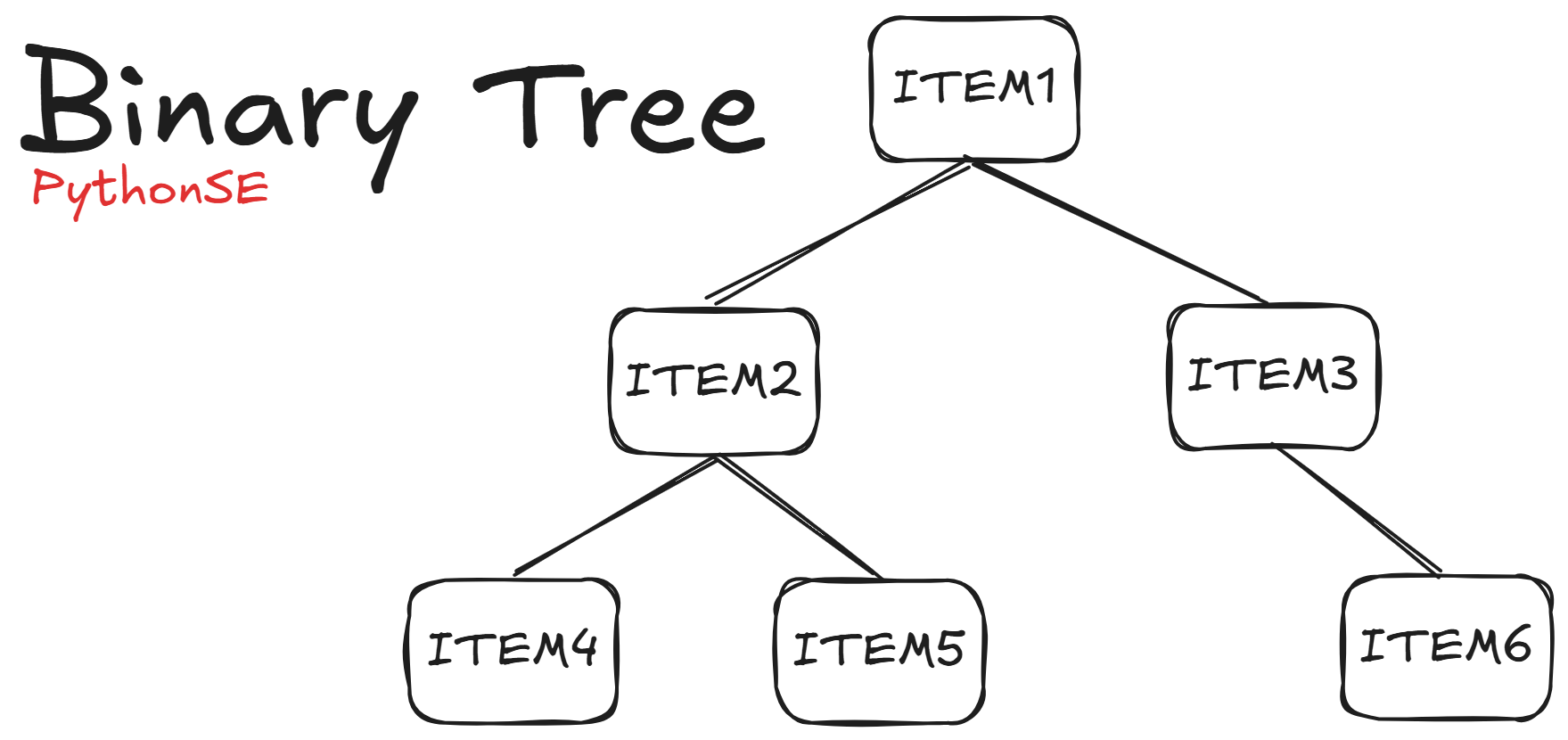
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure in which each node has at most two children, referred to as the left child and the right child. This structure is widely used in various applications, such as expression parsing, sorting algorithms, and database indexing.
Key components of a binary trees:
- Root Node: The topmost node in the tree.
- Leaf Nodes: Nodes that do not have any children.
- Internal Nodes: Nodes with at least one child.
- Subtrees: A tree consisting of a node and its descendants.
In a Binary Search Tree (BST), a special configuration of a binary tree, the left child contains nodes with values less than the parent node, and the right child contains nodes with values greater than the parent node. This property enables efficient searching and sorting.
Implementation
Below is a Python implementation of a BST.
from typing import Optional, List
class Node:
"""Represents a single node in the binary search tree."""
def __init__(self, value: int) -> None:
self.value: int = value # The value stored in the node
self.left: Optional[Node] = None # Pointer to the left child node
self.right: Optional[Node] = None # Pointer to the right child node
class BinarySearchTree:
"""Represents the binary search tree structure.
Ensures that all nodes follow the binary search tree property:
for each node, all values in its left subtree are less, and all values in its right subtree are greater or equal.
"""
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.root: Optional[Node] = None # The root node of the binary search tree (initially empty)
def insert(self, value: int) -> None:
"""Inserts a value into the binary search tree.
Args:
value (int): The value to insert into the tree.
"""
if self.root is None:
self.root = Node(value) # Set the root to a new node if the tree is empty
else:
self._insert(self.root, value)
def _insert(self, current: Node, value: int) -> None:
"""Recursively inserts a value into the correct position in the tree.
Args:
current (Node): The current node being examined.
value (int): The value to insert into the tree.
"""
if value < current.value:
if current.left is None:
current.left = Node(value) # Create a new node if the left child is empty
else:
self._insert(current.left, value) # Recur to the left subtree
else:
if current.right is None:
current.right = Node(value) # Create a new node if the right child is empty
else:
self._insert(current.right, value) # Recur to the right subtree
def inorder(self) -> List[int]:
"""Performs an in-order traversal of the tree.
Returns:
List[int]: A list of node values in ascending order.
"""
return self._inorder(self.root)
def _inorder(self, node: Optional[Node]) -> List[int]:
"""Recursively performs an in-order traversal.
Args:
node (Optional[Node]): The current node being examined.
Returns:
List[int]: A list of node values in ascending order.
"""
if node is None:
return []
return self._inorder(node.left) + [node.value] + self._inorder(node.right)
def search(self, value: int) -> bool:
"""Searches for a value in the binary search tree.
Args:
value (int): The value to search for.
Returns:
bool: True if the value exists in the tree, False otherwise.
"""
return self._search(self.root, value)
def _search(self, current: Optional[Node], value: int) -> bool:
"""Recursively searches for a value in the tree.
Args:
current (Optional[Node]): The current node being examined.
value (int): The value to search for.
Returns:
bool: True if the value is found, False otherwise.
"""
if current is None:
return False # Value not found
if value == current.value:
return True # Value found
elif value < current.value:
return self._search(current.left, value) # Search in the left subtree
else:
return self._search(current.right, value) # Search in the right subtree
#################
# Example usage #
#################
if __name__ == "__main__":
bst = BinarySearchTree()
bst.insert(10) # Insert root node with value 10
bst.insert(5) # Insert value 5 to the left of 10
bst.insert(15) # Insert value 15 to the right of 10
bst.insert(7) # Insert value 7 to the right of 5
# Print the in-order traversal (sorted order of elements)
print(bst.inorder()) # Output: [5, 7, 10, 15]
# Search for specific values in the tree
print(bst.search(7)) # Output: True (7 exists in the tree)
print(bst.search(3)) # Output: False (3 does not exist in the tree)