[Python SE] How does a queue work?

Queues are linear data structures used to manage collections of elements. There are several types of queues; here, we'll look at three of them: standard queues, priority queues, and circular queues.
The fundamental operations that define a queue are:
- Enqueue: Add an item to the back of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove the item from the front of the queue.
Standard Queue
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) principle. Imagine a line at a coffee shop: the first person to arrive gets served first, and each subsequent person must wait their turn. This is exactly how a standard queue behaves: items are added to the back and removed from the front. Python provides several ways to implement a standard queue, the simplest of which is using collections.deque.
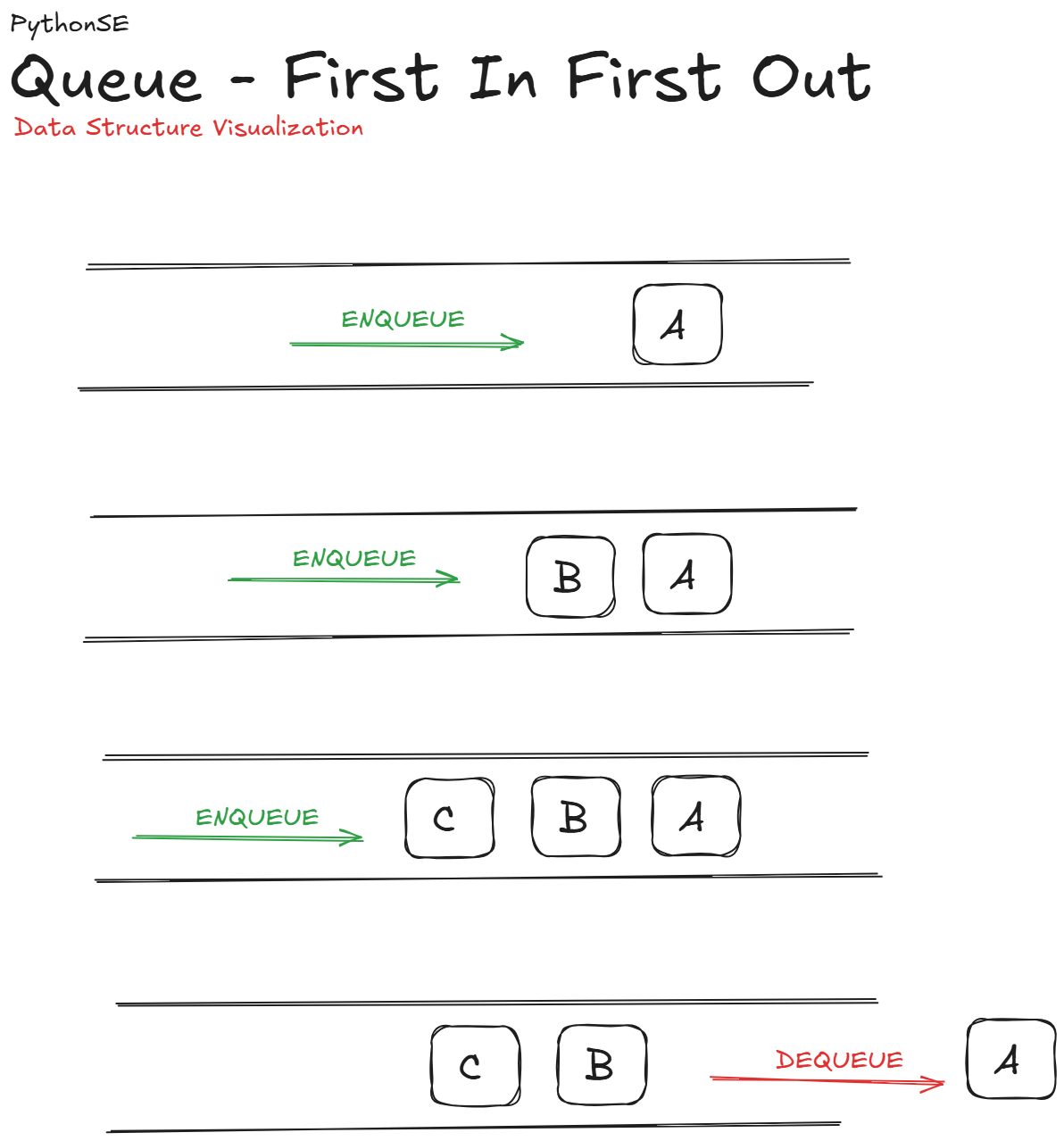
Implementation
class StandardQueue:
def __init__(self):
from collections import deque
self.queue = deque()
def enqueue(self, item):
"""Add an item to the back of the queue."""
self.queue.append(item)
def dequeue(self):
"""Remove and return the front item from the queue."""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Dequeue from an empty queue.")
return self.queue.popleft()
def is_empty(self):
"""Check if the queue is empty."""
return len(self.queue) == 0
def peek(self):
"""Return the front item without removing it."""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Peek from an empty queue.")
return self.queue[0]
# Example usage:
my_queue = StandardQueue()
print("Enqueue A B C")
my_queue.enqueue("A");
my_queue.enqueue("B");
my_queue.enqueue("C")
print(f"Dequeue: {my_queue.dequeue()}") # Dequeue: "A"
print(f"Empty? {my_queue.is_empty()}") # Empty False
Priority Queue
A priority queue allows elements to be dequeued not by arrival order but by their priority. Consider a hospital emergency room, where patients are treated based on the severity of their condition rather than the order of their arrival. This data structure uses an associated priority value for each element, so higher-priority tasks are processed before lower-priority ones.
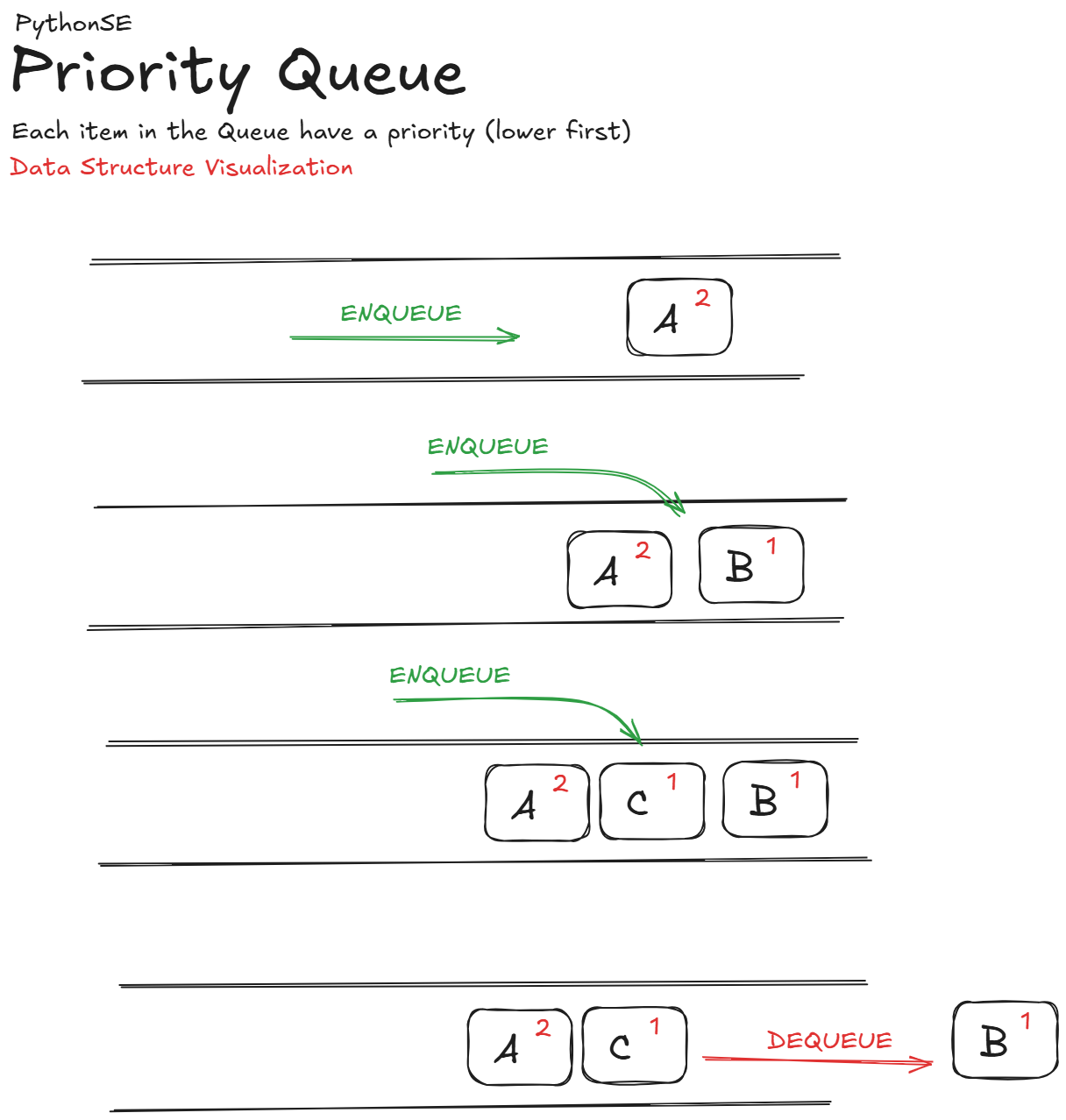
Implementation
class PriorityQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
def enqueue(self, item, priority):
"""Add an item to the queue with the given priority."""
self.queue.append((priority, item))
self.queue.sort(key=lambda x: x[0]) # Keep the queue sorted by priority (lowest first)
def dequeue(self):
"""Remove and return the item with the highest priority."""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Dequeue from an empty queue.")
return self.queue.pop(0)[1] # Remove and return the item with the lowest priority value
def is_empty(self):
"""Check if the queue is empty."""
return len(self.queue) == 0
# Example usage:
my_queue = PriorityQueue()
my_queue.enqueue('A', 2)
my_queue.enqueue('B', 1)
my_queue.enqueue('C', 1)
print(f"Dequeue: {my_queue.dequeue()}") # Dequeue: "B"
print(f"Empty? {my_queue.is_empty()}") # Empty False
Circular Queue
A circular queue differs from a standard queue in that it treats the underlying data storage as a circle rather than a straight line. This prevents wasted space in the memory, as items wrap around when they reach the end of the available space.
A circular queue can be thought of as an amusement park ride: when the cars reach the end of the track, they come back to the start. Circular queues are useful for buffer management, like audio data processing or managing memory in hardware.
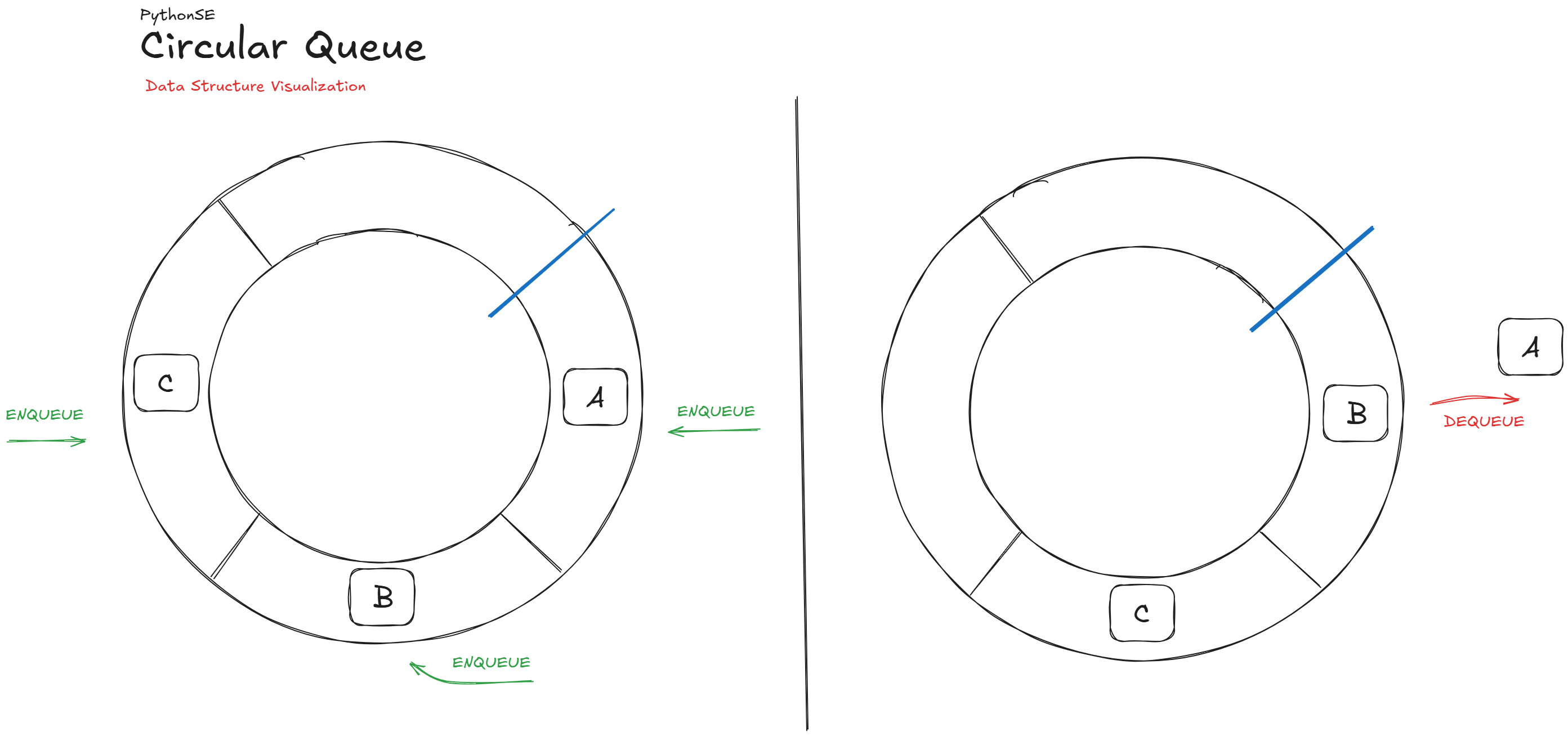
Implementation
class CircularQueue:
def __init__(self, capacity):
"""Initialize the queue with a fixed capacity."""
self.queue = [None] * capacity
self.capacity = capacity
self.front = 0
self.rear = 0
self.size = 0
def enqueue(self, item):
"""Add an item to the next available position."""
if self.size == self.capacity:
raise OverflowError("Queue is full.")
self.queue[self.rear] = item
self.rear = (self.rear + 1) % self.capacity
self.size += 1
def dequeue(self):
"""Remove and return the front item of the queue."""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Dequeue from an empty queue.")
item = self.queue[self.front]
self.queue[self.front] = None # Clear the slot
self.front = (self.front + 1) % self.capacity
self.size -= 1
return item
def is_empty(self):
"""Check if the queue is empty."""
return self.size == 0
def is_full(self):
"""Check if the queue is full."""
return self.size == self.capacity
# Example usage:
my_queue = CircularQueue(3)
my_queue.enqueue('A')
my_queue.enqueue('B')
my_queue.enqueue('C')
print(f"Full? {my_queue.is_full()}") # Full? Trye
print(f"Dequeue: {my_queue.dequeue()}") # Dequeue: "B"
print(f"Full? {my_queue.is_full()}") # Full? False