[Python SE] How does a Heap work?
27/01/25 - #softwareengineering #pyhton #linkedlists
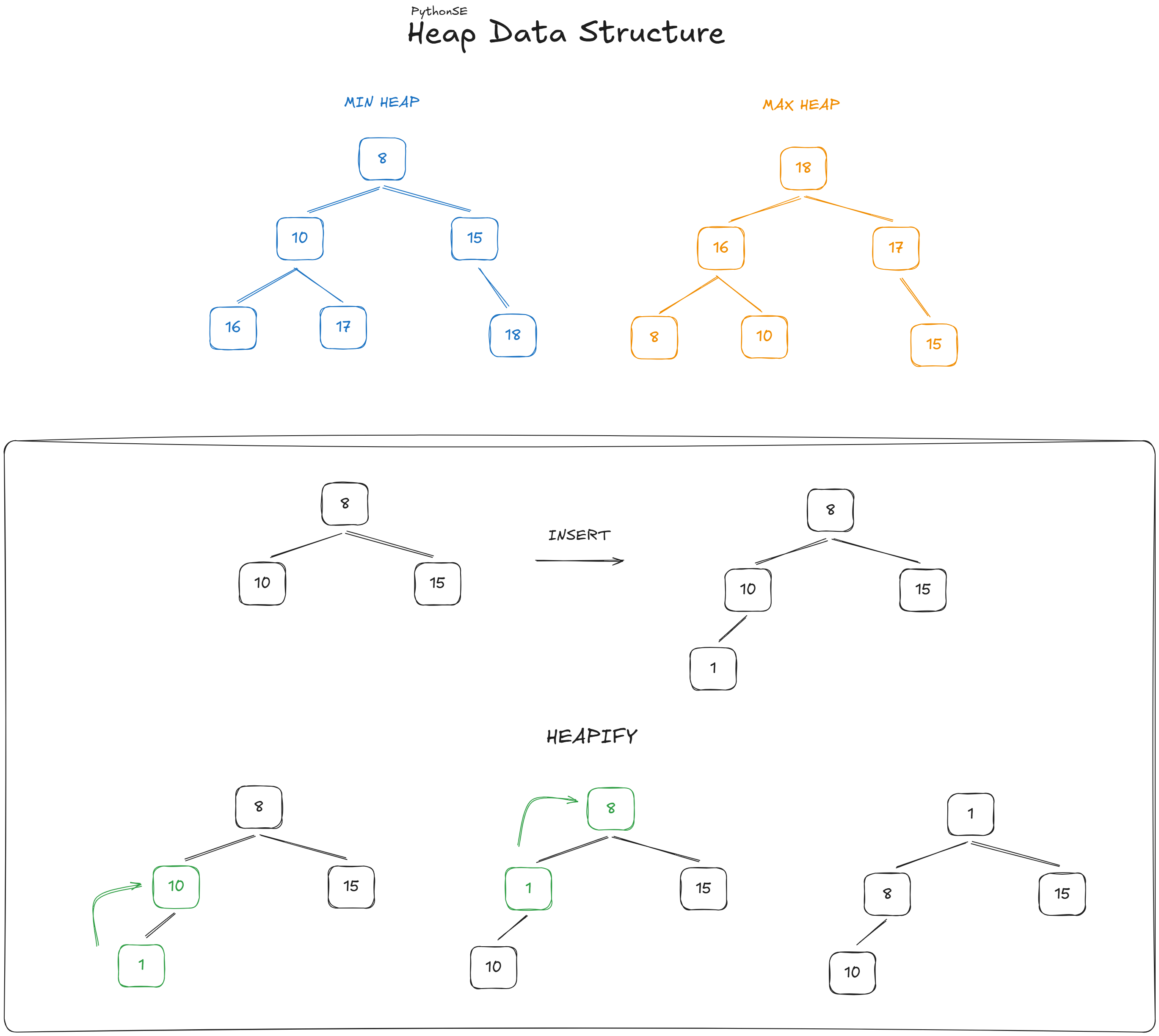
A a heap is a specialized binary tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property. Heaps are commonly used to implement priority queues and for efficient sorting algorithms like heapsort.
But what is the heap property? This depends on the type of tree we are going to build. Here are the two options:
- - For a Max Heap, the value of each node is greater than or equal to the values of its children.
- - For a Min Heap, the value of each node is less than or equal to the values of its children.
The heapify function is a crucial operation that ensures the heap property is maintained. It works by adjusting the positions of elements in a subtree so that the heap property holds, starting from a specific node and propagating the adjustments either upwards or downwards, depending on the context (e.g., for insertion or deletion). This operation runs in O(log n) time for a heap with 𝑛 elements.
Max Heap Implementation
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize an empty Max Heap.
"""
self.heap = []
def _parent(self, index):
"""
Get the index of the parent node.
"""
return (index - 1) // 2
def _left_child(self, index):
"""
Get the index of the left child node.
"""
return 2 * index + 1
def _right_child(self, index):
"""
Get the index of the right child node.
"""
return 2 * index + 2
def _heapify_up(self, index):
"""
Restore the heap property by moving the node at index up.
"""
parent = self._parent(index)
if index > 0 and self.heap[index] > self.heap[parent]:
# Swap with the parent if the current node is greater
self.heap[index], self.heap[parent] = self.heap[parent], self.heap[index]
self._heapify_up(parent)
def _heapify_down(self, index):
"""
Restore the heap property by moving the node at index down.
"""
largest = index
left = self._left_child(index)
right = self._right_child(index)
# Check if the left child is larger
if left < len(self.heap) and self.heap[left] > self.heap[largest]:
largest = left
# Check if the right child is larger
if right < len(self.heap) and self.heap[right] > self.heap[largest]:
largest = right
# If the largest is not the current node, swap and continue heapifying
if largest != index:
self.heap[index], self.heap[largest] = self.heap[largest], self.heap[index]
self._heapify_down(largest)
def insert(self, value):
"""
Insert a new value into the heap.
"""
self.heap.append(value)
self._heapify_up(len(self.heap) - 1)
def extract_max(self):
"""
Remove and return the maximum value from the heap.
"""
if not self.heap:
raise IndexError("extract_max() called on empty heap")
# Swap the max with the last element
self.heap[0], self.heap[-1] = self.heap[-1], self.heap[0]
max_value = self.heap.pop()
# Restore the heap property
self._heapify_down(0)
return max_value
# Example usage:
max_heap = MaxHeap()
max_heap.insert(10)
max_heap.insert(20)
max_heap.insert(15)
print("MaxHeap:", max_heap.heap)
print("Extracted max:", max_heap.extract_max())
print("MaxHeap after extraction:", max_heap.heap)
Min Heap Implementation
class MinHeap:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize an empty Min Heap.
"""
self.heap = []
def _parent(self, index):
"""
Get the index of the parent node.
"""
return (index - 1) // 2
def _left_child(self, index):
"""
Get the index of the left child node.
"""
return 2 * index + 1
def _right_child(self, index):
"""
Get the index of the right child node.
"""
return 2 * index + 2
def _heapify_up(self, index):
"""
Restore the heap property by moving the node at index up.
"""
parent = self._parent(index)
if index > 0 and self.heap[index] < self.heap[parent]:
# Swap with the parent if the current node is smaller
self.heap[index], self.heap[parent] = self.heap[parent], self.heap[index]
self._heapify_up(parent)
def _heapify_down(self, index):
"""
Restore the heap property by moving the node at index down.
"""
smallest = index
left = self._left_child(index)
right = self._right_child(index)
# Check if the left child is smaller
if left < len(self.heap) and self.heap[left] < self.heap[smallest]:
smallest = left
# Check if the right child is smaller
if right < len(self.heap) and self.heap[right] < self.heap[smallest]:
smallest = right
# If the smallest is not the current node, swap and continue heapifying
if smallest != index:
self.heap[index], self.heap[smallest] = self.heap[smallest], self.heap[index]
self._heapify_down(smallest)
def insert(self, value):
"""
Insert a new value into the heap.
"""
self.heap.append(value)
self._heapify_up(len(self.heap) - 1)
def extract_min(self):
"""
Remove and return the minimum value from the heap.
"""
if not self.heap:
raise IndexError("extract_min() called on empty heap")
# Swap the min with the last element
self.heap[0], self.heap[-1] = self.heap[-1], self.heap[0]
min_value = self.heap.pop()
# Restore the heap property
self._heapify_down(0)
return min_value
# Example usage:
min_heap = MinHeap()
min_heap.insert(10)
min_heap.insert(20)
min_heap.insert(5)
print("MinHeap:", min_heap.heap)
print("Extracted min:", min_heap.extract_min())
print("MinHeap after extraction:", min_heap.heap)